By Bruno Ducoudré, Xavier Timbeau and Sébastien Villemot
Current account imbalances are at the heart of the process that led to the crisis in the euro zone starting in 2009. The initial years of the euro, up to the crisis of 2007-2008, were a period that saw widening imbalances between the countries of the so-called North (or the core) and those of the South (or the periphery) of Europe, as can be seen in Figure 1.
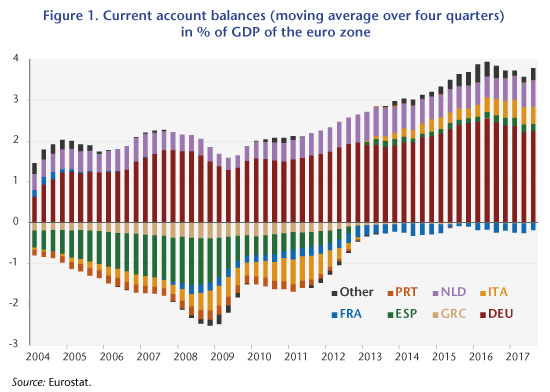
The trend towards diverging current account balances slowed sharply after 2009, and external deficits disappeared in almost all the euro zone countries. Despite this, there is still a significant gap between the northern and southern countries, so there cannot yet be any talk about reconvergence. Moreover, the fact that the deficits have fallen (Italian and Spanish) but not the surpluses (German and Dutch) has radically changed the ratio of the euro zone to the rest of the world: while the zone’s current account was close to balanced between 2001 and 2008, a significant surplus has formed since 2010, reaching 3.3% of GDP in 2016. In other words, the imbalance that was internal to the euro zone has shifted into an external imbalance between the euro zone and the rest of the world, in particular the United States and the United Kingdom. This imbalance is feeding Donald Trump’s protectionism and putting pressure on exchange rates. While the nominal exchange rate internal to the euro zone is not an adjustment variable, the exchange rate between the euro and the dollar can adjust.
It seems unlikely that the euro zone can maintain a surplus like this over the long run. Admittedly, the pressures for the appreciation of the euro are now being contained by the particularly accommodative monetary policy of the European Central Bank (ECB), but when the time comes for the normalization of monetary policies, it is likely that the euro will appreciate significantly. In addition to having a deflationary impact, this could rekindle the crisis in the zone by once again deepening the Southern countries’ external deficits due to their loss in competitiveness. This will in turn give new grounds for leaving the euro zone.
In a recent study [1], we seek to quantify the adjustments that remain to be made in order to resolve these various current account imbalances, both within the euro zone and vis-à-vis the rest of the world. To do this, we estimate equilibrium real exchange rates at two levels. First, from the point of view of the euro zone as a whole, with the idea that the adjustment of the real exchange rate will pass through an adjustment of the nominal exchange rate, notably the euro vis-à-vis the dollar: we estimate the long-term target of euro / dollar parity at US$ 1.35 per euro. Next, we calculate equilibrium real exchange rates within the euro zone, because while the nominal exchange rate between the member countries does not change because of the monetary union, relative price levels allow adjustments in the real exchange rate. Our estimates indicate that substantial misalignments remain (see Figure 2), with the average (in absolute terms) misalignment relative to the level of the euro being 11% in 2016. The relative nominal differential between Germany and France comes to 25%.
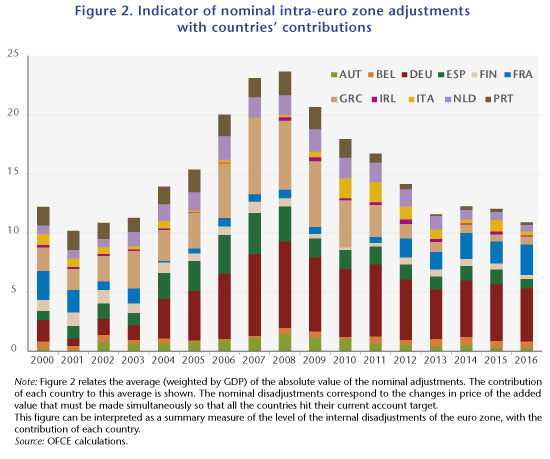
In the current situation, claims by some euro zone countries are not accumulating on others in the zone, but there is accumulation by some euro zone countries on other countries around the world. This time the exchange rate (actual, weighted by accumulated gross assets) can serve as an adjustment variable. The appreciation of the euro would therefore reduce the euro zone’s current account surplus and depreciate the value of assets, which are probably accumulated in foreign currency. France however now appears as the last country in the euro zone running a significant deficit. Relative to the zone’s other countries, it is France that is contributing most (negatively) to the imbalances with Germany (positively). If the euro appreciates, it is likely that France’s situation would further deteriorate and that we would see a situation where the net internal position accumulates, but this time between France (on the debtor side) and Germany (creditor). This would not be comparable to the situation prior to 2012, since France is a bigger country than Greece or Portugal, and therefore the question of sustainability would be posed in very different terms. On the other hand, reabsorbing this imbalance by an adjustment of prices would require an order of magnitude such that, given the relative price differentials that would likely be needed between France and Germany, it would take several decades to achieve. It is also striking that, all things considered, since 2012, when France undertook a costly reduction in wages through the CICE tax credit and the Responsibility Pact, and Germany introduced a minimum wage and has been experiencing more wage growth in a labour market that is close to full employment, the relative imbalance between France and Germany, expressed in the adjustment of relative prices, has not budged.
Three consequences can be drawn from this analysis:
- The disequilibrium that has set in today will be difficult to reverse, and any move to speed this up is welcome. Ongoing moderation in rises in nominal wages in France, stimulating the growth of nominal wages in Germany, restoring the share of German added value going to wages, and continuing to boost the minimum wage are all paths that have been mentioned in the various iAGS reports. A reverse social VAT, or at least a reduction in VAT in Germany, would also be a way to reduce Germany’s national savings and, together with an increase in German social security contributions, would boost the competitiveness of other countries in the euro zone;
- The pre-crisis internal imbalance has become an external imbalance in the euro zone, which is leading to pressure for a real appreciation of the euro. The order of magnitude is significant: it will weigh on the competitiveness of the different countries in the euro zone and will lead to the problems familiar prior to 2012 resurfacing in a different form;
- The appreciation of the euro caused by the current account surpluses in certain euro zone countries is generating an externality for the euro zone countries. Because their current accounts respond differently to a change in relative prices, Italy and Spain will see their current account balance react the most, while Germany’s will react the least. In other words, the appreciation of the euro, relatively, will hit the current accounts of Italy and Spain harder than Germany’s and will lead to a situation of internal imbalance much like what existed prior to 2012. This externality together with the reduced sensitivity of Germany’s current account to relative prices argues for a reduction in imbalances by boosting Germany’s internal demand, i.e. by a reduction in its national savings. The tools to do this could include boosting public investment, lowering direct personal taxes, or raising the minimum wage more quickly relative to productivity and inflation.
Initially published on OFCE’s blog
| [1] | Sébastien Villemot, Bruno Ducoudré, Xavier Timbeau : “Taux de change d’équilibre et ampleur des désajustements internes à la zone euro” [Equilibrium exchange rate and scale of internal misalignments in the euro zone], Revue de l’OFCE, 156 (2018) |